
The benefits of chili pepper: everything you need to know
Chili pepper is a spice widely used in many culinary cultures around the world. This plant belongs to the nightshade family (Solanaceae) and contains a substance called capsaicin, which is responsible for its pungent taste. Not only does it add a spicy flavor to food, but it can also offer health benefits, although some people avoid consuming it because of its effects.
Capsaicin: properties and effects on the human body
Chili pepper is the fruit of a plant from the genus Capsicum, which also includes bell peppers and sweet paprika. It is composed of nitrogenous substances, cellulose, oil, water, mineral salts, and aromatic essence. In terms of health, it contains an impressive number of vitamins and minerals, including A, B6, C, E, K, and PP. It is also a source of minerals and trace elements such as copper, calcium, iron, manganese, magnesium, and potassium. Chili pepper is rich in powerful antioxidants, including luteolin and quercetin. These two flavonoid molecules provide enormous cellular benefits by combating oxidative stress caused by free radicals, which are often linked to diseases and other disorders.
Chili seeds contain an active principle called capsaicin. Capsaicin is the chemical compound that gives this plant its burning effect when consumed raw, cooked, or as a condiment. The hotter the pepper, the higher its capsaicin concentration. Capsaicin also has applications in medicine and natural health.
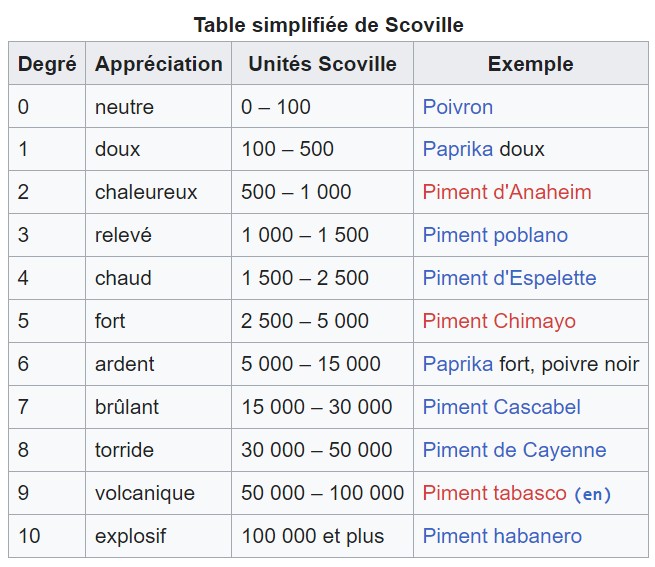
Scoville scale
The Scoville scale is a measurement scale for the heat of peppers, invented in 1912 by the pharmacologist Wilbur Scoville while working for Parke-Davis. Its purpose is to indicate the pungency of different pepper varieties.
Health benefits of chili pepper
Chili pepper has numerous health benefits, including analgesic, preventive, and weight-loss effects.

Effects on digestion and gut flora
It is a real asset for digestion thanks to its ability to stimulate gastric juice secretion. It thus promotes the digestion of foods. Moreover, its capsaicin content has anti-inflammatory properties that help relieve stomach and intestinal pain. Chili pepper is also an excellent ally against constipation due to its stimulatory effect on intestinal transit.
Effects on blood circulation and heart health
Chili pepper also has beneficial effects on blood circulation. Capsaicin has vasodilatory properties that can help lower blood pressure, improve circulation, and prevent cardiovascular diseases.
Impact on weight loss and metabolism regulation
Chili pepper is an effective fat burner. Capsaicin can raise our body temperature through its thermogenic function. This increase in body temperature leads to higher energy expenditure, which promotes weight loss and fat elimination. Indeed, many slimming diets include it.
Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects
Finally, this fruit also has anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties, which can help strengthen the immune system and prevent infections. Research has shown that capsaicin, the main component of chili peppers, may even have a protective role against certain types of cancer.
Use in conventional medicine
Conventional medicine uses chili pepper to relieve peripheral neuropathic pain. Capsaicin’s ability to act on heat receptors of the TRPV1 type in the nervous system gives it this utility.
Use in natural medicine
In natural medicine, capsaicin is used to relieve muscular and joint pain. It is used to treat osteoarthritis, arthritis, and rheumatism.
Despite its positive effects, care must be taken regarding side effects.
Risks and precautions related to chili consumption
Before starting to consume chili pepper, we recommend learning about possible side effects. Indeed, it presents some risks:
Allergic reactions
You may experience allergic reactions to chili. Minor reactions can include redness, itching, burning sensations, nasal discharge, sneezing, tearing, as well as conjunctivitis and other conditions. More severe reactions such as breathing difficulties, airway closure, significant swelling of the throat, eyes, mouth, or entire face may occur. The most severe reaction is anaphylaxis, which is a generalized, life-threatening allergic reaction with risk of recurrence.
Effects on stomach and ulcers
Due to their irritant nature, hot peppers can cause heartburn and acid reflux. They irritate the stomach lining, causing gastric juices to move up into the esophagus, leading to a burning sensation in the chest. Their consumption can also worsen heartburn and ulcers.
Hemorrhoid inflammation
One cause of hemorrhoidal disease is the consumption of spicy and hot dishes. Accordingly, eating spicy food can irritate hemorrhoids and lead to symptoms such as bleeding, pain, and prolapse.
Skin irritation
There are slimming creams containing “chili” that promise inch loss. These creams generally cause tingling or burning sensations due to capsaicin. In reality, very hot peppers are cutaneous irritants and can cause skin lesions with prolonged exposure. Rashes, itching, and severe burning pain are sensations you may experience if chili contacts your skin.
Interaction with certain medications
According to Passeport Santé, cayenne pepper may interact with certain medications or active ingredients:
- In large amounts, cayenne may increase the absorption of theophylline, a medication prescribed for asthma;
- Cayenne may increase coughing in people taking ACE inhibitors (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors);
- Some sources mention a theoretical interaction between cayenne and MAOIs or antihypertensive medications.
How to consume chili pepper
Chili pepper can be used in a variety of dishes, from soups and main courses to sauces and marinades. It is also commonly used in African, Mexican, Indian, Asian, and Thai cuisines. If you are not accustomed to it, start with small amounts and gradually increase over time. You can also add it to soups, salads, and stews.
Besides the flaked form, you can also buy chili in powdered or sauce form, making it easier to integrate into dishes.
In Africa, it is used in almost every dish. Chili-based pastes or sauces combined with other spices or condiments are also common accompaniments.
Different varieties of chili pepper
To help you choose your chili, here is a brief list of the different varieties available.
Espelette pepper

It is grown in the small commune of Espelette in the heart of the Basque Country. On the Scoville scale, the Espelette pepper scores a 4.
Jalapeño pepper

Originating from South America, it is cultivated around the city of Jalapa in the state of Veracruz. On the Scoville scale, it is rated a 5.
Cayenne pepper

It is named after the capital of French Guiana, where it was discovered by early Spanish explorers. Widely used in African, American, and Asian cuisines, the Scoville scale rates it a 6.
Chiltepin pepper

This Mexican-origin pepper is mainly used in sauces. The Scoville rating for arbol chili is 7.
Bird’s eye chili

Widely used in South American, Asian, Caribbean, and Réunionese cuisine, this pepper is small but very powerful. On the Scoville scale, bird’s eye chili scores an 8.
Tabasco pepper

Used in the famous Tabasco sauce, this chili has flavors of onion and celery. The sauce itself is less intense than the raw pepper. On the Scoville scale, it rates a 9.
Habanero pepper

Known as one of the hottest peppers in the world, it is found in the Caribbean, Africa, and beyond. The Scoville scale rates habanero pepper at 10.
Carolina Reaper

With a capsaicin value between 1,500,000 and 2,200,000 SHU, the Carolina Reaper is indisputably THE hottest pepper in the world. Its aroma may seem fruity and slightly citrusy, but it quickly gives way to intense heat.
In summary, despite its potentially irritating effects, chili pepper should not be underestimated for its many health virtues. Whether to aid digestion, improve circulation, burn fat, or strengthen the immune system, chili pepper offers multiple benefits to our body. Of course, it is important to consume it in moderation to avoid unwanted side effects.
At SennaCare, we connect you with healthcare professionals who can guide you in your diet. We also encourage our users to learn more about nutrition.
